Specific Heat of Different Materials Is Different Explain
However attributing this to the heat capacity of specific atoms is not quite precise. Specific Heat Capacity of Materials Specific heat or specific heat capacity is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics.

Tabulated Specific Heat Capacity Of Sapphire Reference Material And Download Table
Based on your observations analysis from above explain what you would expect to see when you research the Specific Heat Capacity value for copper.

. The relationship between heat and temperature can be expressed as. The specific heat is the amount of heat necessary to change the temperature of 100 kg of mass by 100 ºC. The specific heat of water is 4186 Jg-1o C-1 in easy words we can say that to make the increase of 1 o C in 1 gram of water we require 4186 Joule heat energy.
With all other factors equal which requires the most energy to heat equal masses of A and B to the same temperature. This lesson explains the difference between heat and temperature as well as how to calculate specific. 6V x 02A 12 12 x 600s 720 J 720J17C 42 J.
Thus the element having lower atomic mass has higher specific heat capacity. Al 0903 JgC Pb 0160 JgC. 172 rows Related Topics.
Conduct research to find the specific heat capacity of water and iron 14. The intensive properties c v and c p are defined for pure simple compressible substances as partial derivatives of the internal energy uT v and enthalpy hT p respectively. If equal heat is provided to both the samples because of difference in the number of molecules the average kinetic energy will become more for the one which has less number of molecules.
Use this chart showing the different specific heat of various materials to answer the questions. The symbol c stands for specific heat and depends on the material and phase. 0 o C to 1 5 o C.
6V x 02A 12 12 x 600s 720 J 720J16C 46 J 45J1000 0045 JgC 3dp Iron. 2 0 0. Heat capacity is an extensive propertyit depends on the amount or mass of the sample.
1 4 T 0. The intensive properties c v and c p are defined for pure simple compressible substances as partial derivatives of the internal energy uT v and enthalpy hT p respectively. Explain whether the washer did the.
Material Properties - Material properties of gases fluids and solids - densities specific heats viscosities and more. Air - Specific Heat vs. Pressure at Constant Temperature - Figures and tables with isobaric Cp and isochoric Cv specific heat of air at constant temperature.
Where m is the mass of the substance and Δ T is the change in its temperature in units of Celsius or Kelvin. Different materials have different specific heat capacities. The specific heat capacity of a material is the relative amount needed to raise its temperature.
6V x 02A 12 12 x 600s 720J 720J9C 80J 80J995g 008 JgC 3dp Brass. Thermodynamics - Work heat and energy systems. Q m c Δ T 117.
Q cm T where Q is Heat Added C is Specific Heat T is change in temperature. Because the specific heat capacity is different for different materials and. Both require the same amount of heat.
Therefore in engineering applications you might find that the term 𝜌𝑐does not differ drastically between different materials. Different substances have different heat capacities which are all calculated differently. The main objective of the specific heat of metalslab was to compare the specific heat of the different metals find the theoretical and experimental values and describe the transfer of heat when the metals are transferring heat to its surrounding room temperature waterWe used a few different metals for this experiment.
For many materials if the density of a material is high the specific heat of the material is comparatively low. Water is also pretty high since it has a couple bonds lots of intermolecular forces and isnt very heavy. This rule does not apply to.
Material JkgK BtulbmF JkgC kJkgK Aluminium 887 0212 887 0887 Asphalt 915 021854 915 0915 Bone 440 0105 440 044 Boron 1106 0264 1106 1106 Brass 920. Specific heat is defined as the amount of heat required to increase the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius. Substance A has a higher specific heat than substance B.
The specific heat of a substance varies with temperature according to the function c 0. If I have 3 materials and mixed it can I compute for the specific heat of the mixed material. Specific heat capacity is the amount of energy you have to put into a substance to raise a kg of it by 1 degree C or K.
The specific heat capacity of materials ranging from Water to Uranium has been listed below in alphabetical order. 0 2 3 T 2 with T in o C and c in c a l g. Which material has the lowest specific heat.
I have the data of the specific heat of each of the material and the precentage by weight. It is due to the kinetic energy of atoms in gases. It can be defined as the quantity of heat required to raise the temperature of one gram of a substance by one degree Celsius or one Kelvin at a constant pressure The unit of specific heat is Jg-1o C-1.
0 g of this substance from 5. Hydrogen gas for example has an internal bond between two very light atoms and thus exceptionally high specific heat. In fact mechanisms governing heat capacity in gases metals and isolatorssemiconductors are quite different.
Specific heat or specific heat capacity s is the heat capacity which is independent of the amount of substances. Find the energy required to raised the temperature of 2. For example the molar mass of copper is 6355 gmol and the molar mass of sulfur is 3207 gmol therefore in 1g of sulfur there will be twice as many atoms as in 1g of copper and therefore the specific heat capacity of sulfur will be higher 073 JgC than the specific heat capacity of copper 0385 JgC.
Answer depends on the density of each substance. The quantity of heat added or removed to produce a given change in temperature depends on the amount of material involved mass and specific heat capacity. It is primarily due to the conduction electron energy in metals.
Heat energy required to heat the mass of metal by 1C J Specific heat capacity of metal joules per gram JgC Aluminum. Material 1 is 46 of the total weight material 2 is 52 and material 3 is 2 cd 0464186 05234 00243 _____ thanks in advance. Below this table is an image version for offline viewing.
Specific Heat of Materials Specific heat or specific heat capacity is a property related to internal energy that is very important in thermodynamics. The specific heat capacity of copper is this means 16. Specific heat is a measure of the heat capacity of a substance.
So the highest heat capacities come in things with some internal degrees of freedom and very light atoms. A lead B wood C water Which material has the ability to absorb twice as much heat as aluminum when placed in the same environment of mass and temperature.
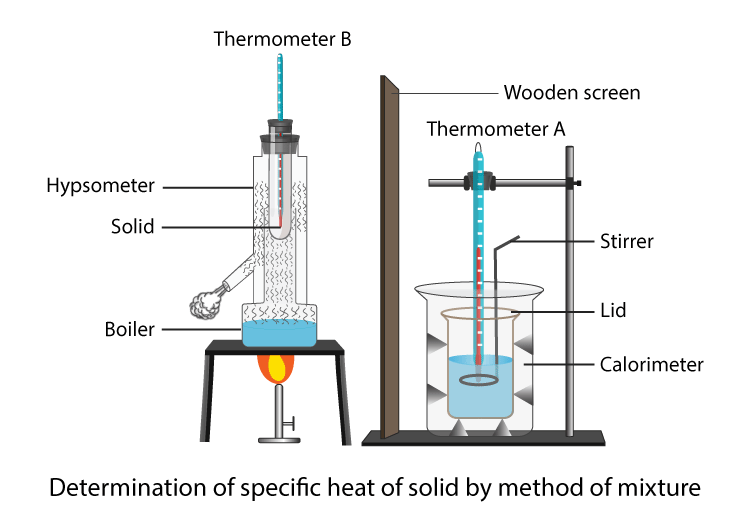
To Determine Specific Heat Capacity Of A Given Solid Physics Practical
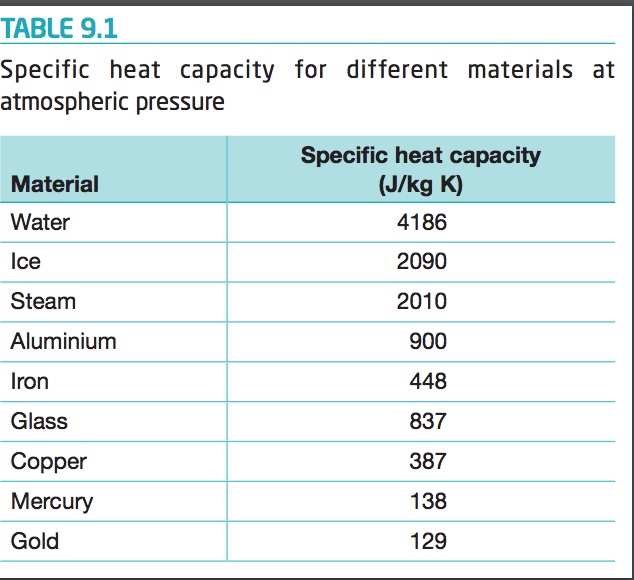
Solved Table 9 1 Specific Heat Capacity For Different Chegg Com

Heat Capacity An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
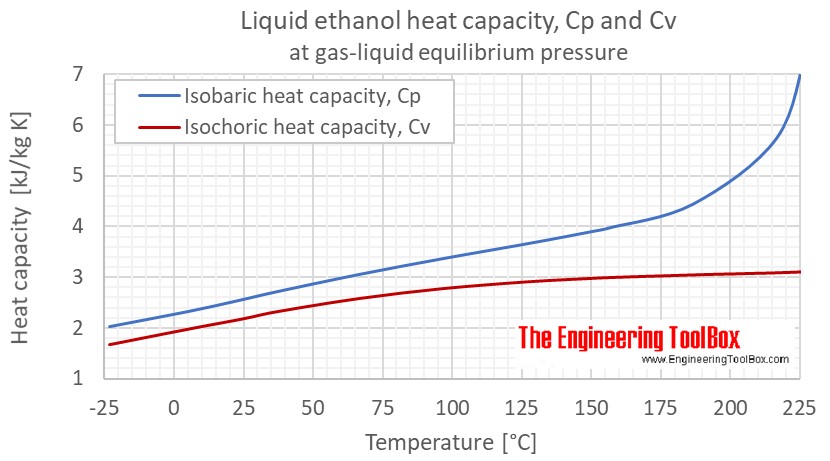
Ethanol Specific Heat Vs Temperature And Pressure

Specific Heat Capacity Of Materials The Engineering Mindset

Heat A Simple Introduction To The Science Of Heat Energy

Specific Heat Boundless Physics

Specific Heat Of Water Very High So It Takes More Energy To Increase The Temperature Of A Given Mass Of Wat Teaching Science Science Facts Homeschool Science

Specific Heat Capacity Matter Physics Fuseschool Youtube

Can Anyone Suggest A Material With The Highest Specific Heat Capacity Higher Than Water

How Do The Specific Heats Of Metals Compare With Water Socratic Heat Methylation Water
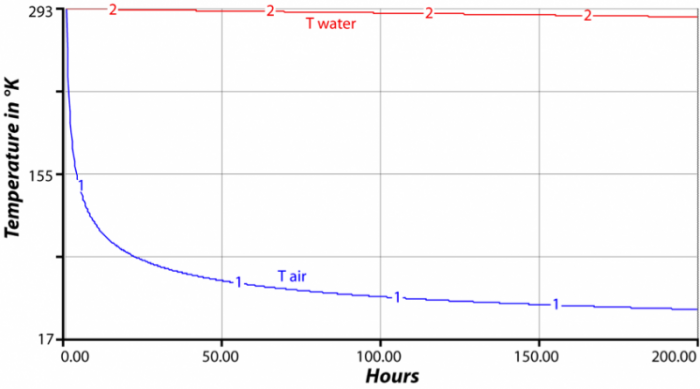
Heat Capacity And Energy Storage Earth 103 Earth In The Future

Specific Heat Boundless Physics
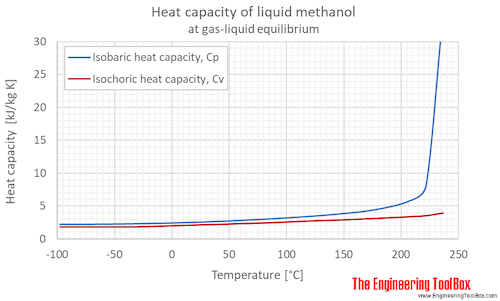
Methanol Specific Heat Vs Temperature And Pressure
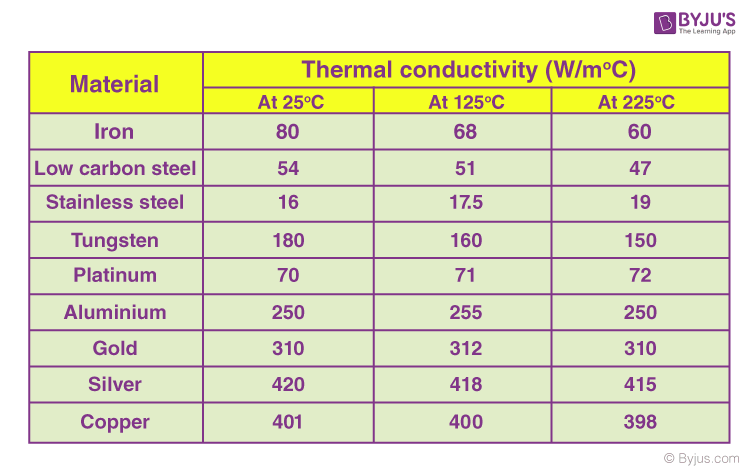
Thermal Properties Of Materials Physical Properties Of Materials Byjus
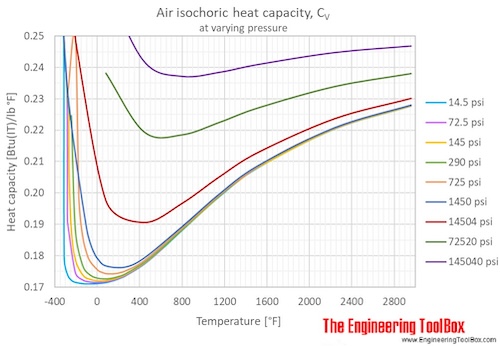
Air Specific Heat Vs Temperature At Constant Pressure

Specific Heat Capacity Definition Molar Specific Heat Videos Examples

Specific Heat Definition Facts Britannica

Tabulated Specific Heat Capacity Of Sapphire Reference Material And Download Table